Articles & News
NanoCoulter™ Empowers Breakthrough Exosome Research in Cutting-Edge Biomedical Studies
Exosomes—tiny messengers for cell-to-cell communication—are emerging as powerful tools in diagnostics, therapeutics, and drug delivery. Yet their precise characterization remains challenging, as traditional optical methods lack the resolution to analyze them at the single-particle level. NanoCoulter™, based on resistive pulse sensing (RPS), delivers high-sensitivity, high-resolution analysis comparable to electron microscopy—enabling detailed exosome profiling with ease.
Recently, NanoCoulter™ has recently gained increasing recognition in the scientific community, with several studies citing and validating its benefits for exosome characterization. Below are highlights from a few representative research papers.
Platycodon grandiflorum-derived extracellular vesicles suppress triple-negative breast cancer growth by reversing the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and modulating the gut microbiota.
Platycodon grandiflorum-derived extracellular vesicles (PGEVs) were investigated for their therapeutic efficacy against triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). The study demonstrated that PGEVs inhibit tumor proliferation, induce apoptosis, promote macrophage M1 polarization, and modulate the gut microbiome—significantly suppressing TNBC growth.
NanoCoulter™ was used to characterize the particle size and zeta potential of PGEVs, confirming their stability (average size: 74 nm; zeta potential: –19.23 mV). These results supported PGEVs as a biocompatible nanotherapeutic candidate for TNBC treatment.
Reference:Yang M, Guo J, et al. J Nanobiotechnology, 2025.
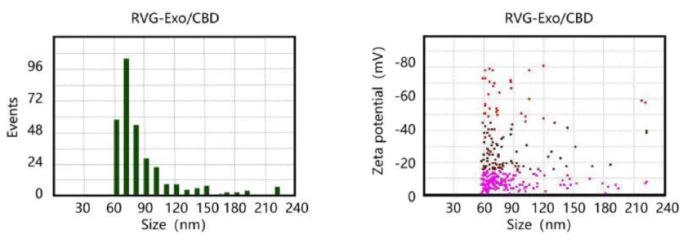
Houttuynia cordata-Derived Exosome-Like Nanoparticles Mitigate Colitis in Mice via Inhibition of the NLRP3 Signaling Pathway and Modulation of the Gut Microbiota.
This study focused on exosome-like nanoparticles derived from Houttuynia cordata (HELNs) for treating DSS-induced colitis in mice. HELNs effectively targeted inflamed colon tissues, modulated the immune microenvironment, and suppressed the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. The particles also helped restore gut microbiota balance.
TEM and NanoCoulter™ were jointly employed to measure particle size and concentration. A wide distribution of HELNs (60–200 nm) was observed, highlighting the method’s precision and importance in preclinical profiling.
Reference: Li J, Xu J, et al. Int J Nanomedicine, 2024.
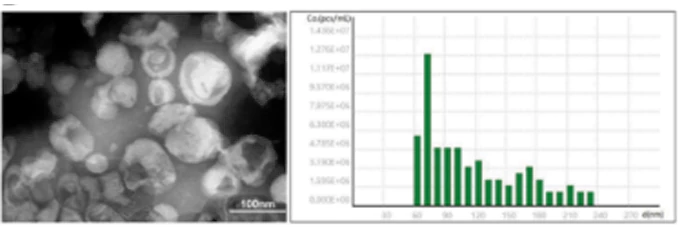
Exosomes Derived from Antler Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Wound Healing by miR-21-5p/STAT3 Axis.
In a recent study on exosomes derived from antler mesenchymal stem cells (AMSC-Exo), researchers explored their biological activity, mechanisms of action, and therapeutic potential. AMSC-Exo was found to promote the proliferation and migration of HaCaT cells (human immortalized keratinocytes) and enhance the migration and angiogenesis of HUVECs (human umbilical vein endothelial cells). In a murine full-thickness skin wound model, AMSC-Exo facilitated the transition from type III to type I collagen, stimulated angiogenesis, and regulated the extracellular matrix, leading to normalized epidermal thickness without abnormal hyperplasia. Notably, AMSC-Exo improved wound healing quality by enhancing vascularization and reducing scar formation.
The study employed NanoCoulter™ to precisely measure the particle size distribution and zeta potential of AMSC-Exo. These data were critical for understanding the physical characteristics and colloidal stability of the exosomes, providing a solid foundation for their future biomedical applications.
Reference: Meng D, Li Y, et al. Int J Nanomedicine, 2024.
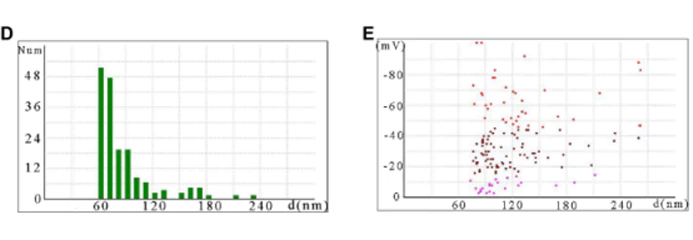
The Cardioprotective Effect of Ginseng Derived Exosomes via Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis.
In a study investigating ginseng-derived exosomes (G-Exo), researchers examined their protective effects and underlying mechanisms against cisplatin (CDDP)-induced cardiotoxicity. The results showed that G-Exo effectively alleviated CDDP-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in vitro. Specifically, G-Exo reduced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, restored mitochondrial membrane potential, and inhibited activation of the MAPK signaling pathway, thereby mitigating apoptosis. In vivo, G-Exo significantly reduced serum levels of cardiac troponin T (cTnT), creatine kinase (CK), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), while also attenuating histopathological damage in cardiac tissue, underscoring its therapeutic potential as a cardioprotective agent against CDDP-induced toxicity.
NanoCoulter™ was employed to precisely characterize the particle size and zeta potential of G-Exo, enabling researchers to verify its size distribution and surface properties. The results demonstrated the excellent stability of G-Exo, supporting its suitability for biomedical applications.
Reference: Yang S, Guo J, et al. ACS Appl Bio Mater, 2024.
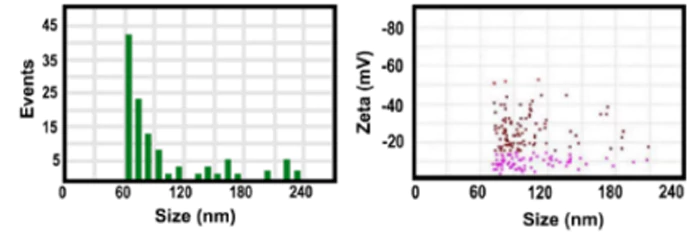
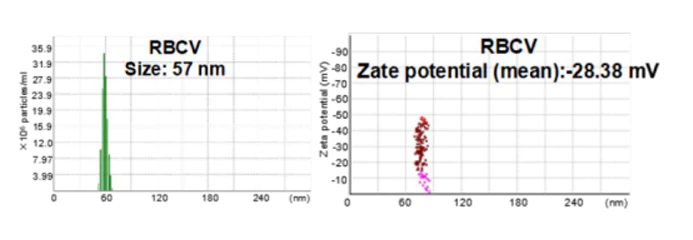
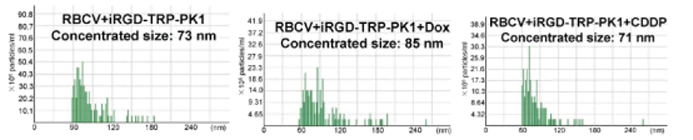
iRGD-TRP-PK1-modified red blood cell membrane vesicles as a new chemotherapeutic drug delivery and targeting system in head and neck cancer.
A novel chemotherapeutic delivery platform used iRGD-TRP-PK1-modified red blood cell membrane vesicles (RBCVs) to target head and neck cancer (HNC). The system ensured drug release within tumor cells by exploiting the high-potassium environment, minimizing off-target toxicity.
NanoCoulter™ provided key insights into particle size, concentration, and zeta potential in different vesicle modification states, enabling optimization of formulation and validating the delivery system’s physical properties.
Reference: Bai S, Wang Z, et al. Theranostics, 2025.
NanoCoulter™: Powering Precision in Nanomedicine and Beyond
From characterizing plant-derived exosomes to advanced drug delivery systems, NanoCoulter™ proves to be a versatile, high-precision tool across disciplines. Its capability to measure particle size, concentration, and single-particle zeta potential allows researchers to generate richer, more reliable data—paving the way for innovations in biomedicine, material science, and beyond.
With continued technological refinement and expanding applications, NanoCoulter™ is poised to become an indispensable instrument in unlocking the secrets of the nanoscale world.